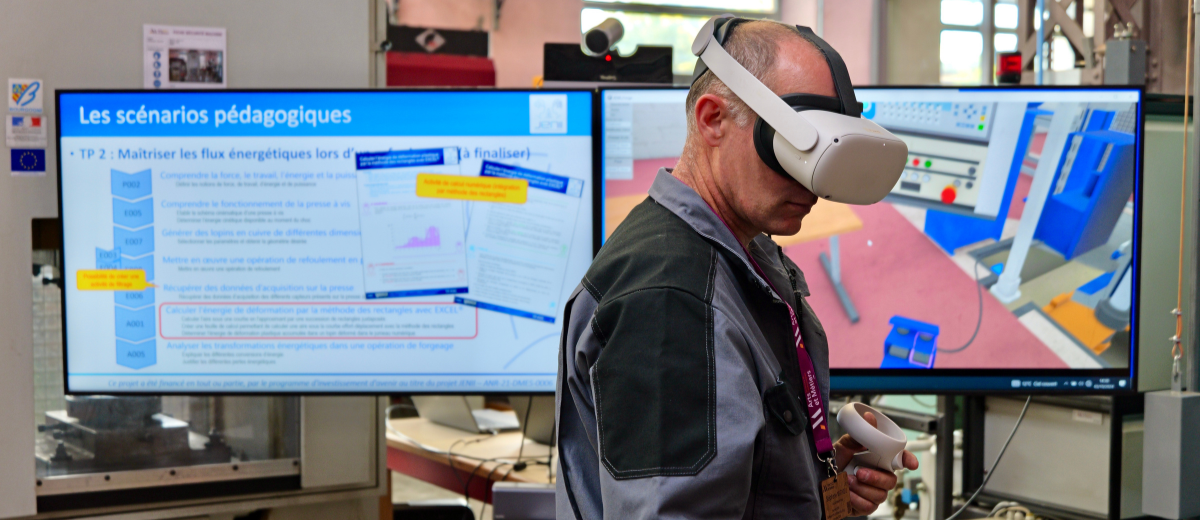
Master’s programme 2 years (Graduate)
AM²S : Advanced Manufacturing and Materials Science (M1+M2)
The Master’s specialization “Advanced Manufacturing and Materials Science” (AM²S) is positioned at the crossroads of France, Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and the U.S. industrial ecosystem, by offering the AM²S courses in English for the Master of Science degree (MSc) and PGE 3rd ENSAM / Master of Engineering (MEng).
The objectives are also to increase students’ knowledge in the field of manufacturing processes and the materials science through multi-physics and multi-scale approaches, including smart and digital concepts. In other words, this program will focus on innovative scientific fields, from the physics and chemistry of materials to the use of manufactured parts, by developing the duality between experimentation and numerical simulation.
Arts et Métiers offers the "Advanced Manufacturing and Materials Science " master to Bachelor of Science or Engineering graduates, in two years.
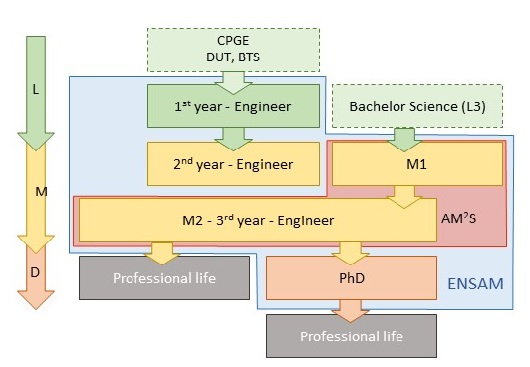
MASTER 1
The Master 1 Specialty “Advanced Manufacturing and Materials Science” for Transport and Energy (AM2S-M1) is directly positioned before a Master 2 course (e.g. AM2S-M2.). The objectives are to prepare engineers for industrial and laboratory research and also to increase their knowledges of the physics of manufacturing processes and the fundamentals of the materials behaviors with an objective to design processes to aim for targeted physical properties. The courses are taught on Aix en Provence campus in association with MSMP lab and the Learning Factories.
The courses are composed of :
- One semester of core courses for 310 h and 30 ECTS based on mandatory teaching units (TUs) during the first semester. These units will allow to the students to get insights in mechanics and material science for manufacturing processes and to understand the relationship between material and processes. A TU will introduce the key skills to write proposals and scientific publications.
- A second semester of courses with the research project in Manufacturing and Material Science (300 h and 30 ECTS). Advanced materials and manufacturing processes will be addressed in order to optimize the processes to a targeted surface integrity (topography, residual fields, microstructure)..
- Individual research internship of 6 to 8 weeks. The internship will be led in a research structure (laboratory of university, research service in the industry). Dates: May-June– 6 ECTS.
Link to M1-AM²S Advanced Manufacturing and Materials Science
MASTER 2
The scientific objectives of the AM²S-M2 program emphasizes a high-level scientific approach by:
- Improving the knowledges of the relationships between the Material Science and the Manufacturing Processes,
- Using multiphysic and multiscale approaches to better understand the relationships between materials/mechanics/processes,
- Mastering the numerical tools for optimizing the design of structures and parts high added value,
- Using new technologies, in particular smart digitalization, big data, and numerical simulations.
These objectives will allow students to move on to a PhD program with knowledge and skills in the materials sciences and/or smart manufacturing.
The courses are composed of:
- Core courses (150 hrs., 15 ECTS) with 5 mandatory teaching units (TUs) during the first semester.
- Two Elective paths (150 hrs., 15 ECTS) with 3 mandatory TUs and 2 elective TUs during the first semester:
- Materials Science elective
- Advanced Manufacturing elective
- Individual research project (30 ECTS) for 6 months during the second semester. The internship will be done in a research structure (university laboratory, research department in a company in the field).
Link to M2-AM²S Advanced Manufacturing and Materials Science
DUAL DEGREE OPTION WITH TEXAS A&M
A dual degree with TAMU for the M1+M2 track where a full academic year at TAMU during the second year is proposed upon academic selection after the first year.
The Dual Degree is with the Master of Science in Interdisciplinary Engineering (ITDE) at TAMU.
The course credits of M1-AM2S are transferred to the Degree of TAMU. 18 Semester Credits Hours have to be completed at TAMU including a research project. The research project counts also for the M2-AM²S.
ADMISSION
- Foreign and French students can apply to the formation
- Bachelor of Science or Engineering graduates only
- Level of English: the minimum requirement is TOEFL iBT 81/120 (or equivalent) or IELTS 6.0
- The selection is based on academic excellence, motivation of the candidate and professional project consistency.
TUITION FEES
First year (M1)
- Tuition fees: 250 EUR / year (students from European Union and out of European Union)
Second year (M2)
- Tuition fees: 240 EUR / year (students from European Union and out of European Union)
Dual Degree option with TAMU (M1+M2)
- Tuition fees for M1 : 250 EUR / year (students from European Union and out of European Union)
- Tuition fees for the Dual Degree at TAMU (year 2) : one complete year with 18 Semester Credits Hours have to be completed at TAMU including a research project.
BioMedical Engineering (M2)
The master's degree in BioMedical Engineering stands at the crossroads of two innovation-rich fields: engineering sciences and biomedicine. This programme is a partnership between the University of Paris Cité and ParisTech – on which Arts et Métiers depends – with additional expertise: life sciences and biomedicine from the Paris university and engineering and technology from ParisTech.
Transdisciplinarity and the international dimension are the two pillars of the BioMedical Engineering master's programme, which caters for students from diverse backgrounds: not only biology, chemistry and health sciences, but also engineering sciences, computer science, mathematics and physics. The main goal is to provide skills in the main biomedical engineering fields, which are increasing in significance in terms of both research and industrial development.
Five specialities are currently on offer to candidates:
Factory of the Future
Arts et Métiers offers the "Factory of the Future" master to Bachelor of Science or Engineering graduates, in two years : the first year is dedicated to fundamental sciences and industrial applications ; the second year is devoted to the specialisation.
Students have the opportunity to get acquainted with the different steps of scientific research project , thanks to scientific immersion within Arts et Métiers’s research units. They develop skills in project management while they are given in-depth education in Engineering Sciences .
When applying, students choose a specialisation among nearly 20 possibilities classified in 3 main orientations (calculation, communication and project management):
- Industrial Engineering
- Energy
- Mechanical Engineering
The 1st year (60 ECTS) is taught on Paris campus. Fully taught in English, it involves 2 blocs namely calculation (Mathematics, Data processing, Numerical methods ), communication & organisation (Bibliography technics, Project management, Scientific communication in English, Career Development and Foreign language (French or English) ).
Students also attend required courses depending on the orientation of the specialisation. An intership in Industry (13 weeks minimum) is also complusory, to help develop professional skills.
A semester dedicated to master thesis
During the 2nd year (60 ECTS), specific theoretical courses are taught during the first semester. Students prepare then their master thesis during the second semester. Classes and master thesis depend on the chosen specialization amongst the 20 possibilities in 3 areas :
- Industrial Engineering
- Energy
- Mechanical Engineering
See our list of specializations
Admission
- Both foreign and French students are eligible to apply to the formation
- Exchange students can only take this master course for the first semester, or for the whole academic year
- Bachelor of Science or Engineering graduates only
- Level of English: the minimum requirement is TOEFL iBT 81/120 (or equivalent) or IELTS 6.0
- The selection is based on academic excellence, motivation of the candidate and professional project consistency.
Tuition fees
First year (M1)
250 EUR / year (students from European Union and out of European Union)
Second year (M2)
250 EUR / year (students from European Union and out of European Union)
MTI3D research master's
The MTI 3D master's programme aims to train experts in 3D interactive technologies. With a combination of laboratory research and application in the field, they are trained to create new products and services based on virtual technology – virtual reality, augmented reality, 3D and connected objects.
Two M2 (second year master's programme) courses are possible : human-machine interactions (at the Chalon-sur-Saône Arts et Métiers institute), innovation perception and management, engineering and advanced virtual reality (in Laval).
This offers many career opportunities: R&D Manager, teacher-researcher, virtual reality or augmented reality engineer, IT project manager, consultant or start-up entrepreneur.
Admission
M1 (first year master's degree course) is accessible with a degree, while M2 can be followed after an M1, another M2 course, a degree in engineering or a final year at engineering school. After their applications have been assessed, selected candidates attend a recruitment interview and take a test in English.







